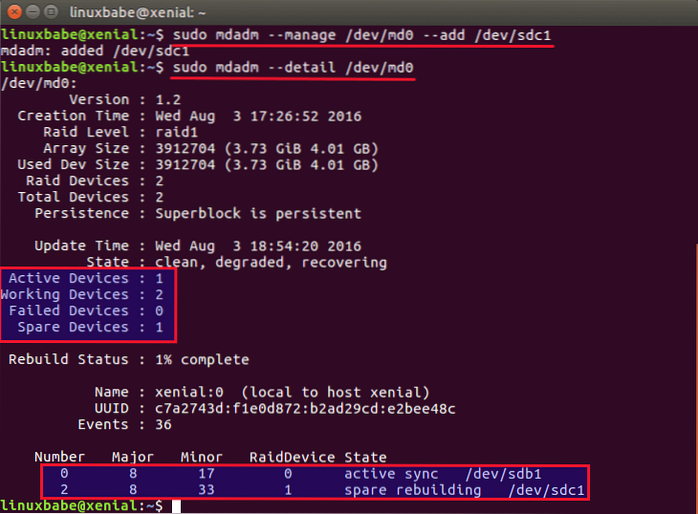
And finally create the RAID 1 array using the mdadm utility.
- Step 1: Format Hard Drive. Insert two hard drives into your Linux computer, then open up a terminal window. ...
- Step 2: Install mdadm. ...
- Step 3: Create RAID 1 Logical Drive. ...
- Step 4: Create File System on the RAID 1 Logical Drive. ...
- Step 5: Test.
- How do I create a RAID 1 with existing disk?
- Can you create a RAID 1 without losing data?
- Can you raid a drive with data on it?
- How do I add a raid to an existing system?
- Can you install OS on RAID 1?
- Can you change raid without losing data?
- Can RAID 1 have more than 2 drives?
- Does RAID 1 delete data?
- How many disks can be used for RAID 1?
- Is RAID 1 good for backup?
- Do you need a separate backup system if you are using RAID?
- Why RAID is not a backup but is part of redundancy?
How do I create a RAID 1 with existing disk?
1 Answer
- First prepare the disk with gdisk since fdisk can not do a partition larger than 2TB. ...
- Run sudo mdadm --create --verbose /dev/md0 --force --level=1 --raid-devices=1 /dev/sdb1 . ...
- Format the newly created RAID partition and copy everything from the original disk to this partition.
Can you create a RAID 1 without losing data?
Many RAID solutions format a disk when constructing a RAID or adding a new disk. Desktop versions of Windows Windows have a built-in software RAID capability which will attempt to preserve your data during conversion. However, you should still back up your data in case something goes wrong.
Can you raid a drive with data on it?
Use the Intel Rapid Storage Technology user interface to create a RAID volume. You can migrate the data from a single hard drive to a RAID volume that includes that hard drive and the new hard drive(s). You can also create a new RAID volume using the newly added hard drives.
How do I add a raid to an existing system?
Adding raid to existing system
- set your SATA controllers to RAID mode in BIOS.
- Boot into windows *may need RAID drivers installed.
- Install the SATA raid utility available from your motherboard's support/driver page.
- Run it and create a new volume with both disks selected.
- You should be prompted to select a data drive then a target copy drive.
Can you install OS on RAID 1?
3 Answers. The RAID configuration is stored on the RAID volumes themselves, so there is no need to worry about copying it. When you install the OS on the new SSD, all you should need to do is install the driver.
Can you change raid without losing data?
Storage pools can be changed from one RAID type to another without losing existing data. For example, you can create a RAID 1 storage pool on your Synology NAS and later change it to RAID 5 if you install more drives.
Can RAID 1 have more than 2 drives?
You can use as many drives as you want for RAID1. They will all be mirrored, and written on at the same time, and be exact copies of each other.
Does RAID 1 delete data?
Data loss can occur if the RAID 1 volume is the second volume in a matrix RAID configuration.
How many disks can be used for RAID 1?
RAID 1 can be implemented through either software or hardware. A minimum of two disks is required for RAID 1 hardware implementations. With software RAID 1, instead of two physical disks, data can be mirrored between volumes on a single disk.
Is RAID 1 good for backup?
One very important thing to note, RAID 1 is not a backup in and of itself. Although RAID writes data to two disks simultaneously, it is not a backup. If your operating system or software, rather than the hard disk, corrupts your data, this corrupted data is sent to both disks and simultaneously corrupts both drives.
Do you need a separate backup system if you are using RAID?
Is RAID a backup? While RAID arrays can provide enhanced data protection, their extra disks should not be considered as backups. If your main drive is a RAID array, you still need to back it up. If you have, say, 12 TB storage on a RAID array, you'll want to back it up to another device.
Why RAID is not a backup but is part of redundancy?
The number one reason you want a backup is not because the physical media died (this is rare), but because of some error that caused the data to be lost or corrupted. RAID doesn't protect you against a file being deleted. RAID doesn't protect you against a file being overwritten.
 Linuxteaching
Linuxteaching